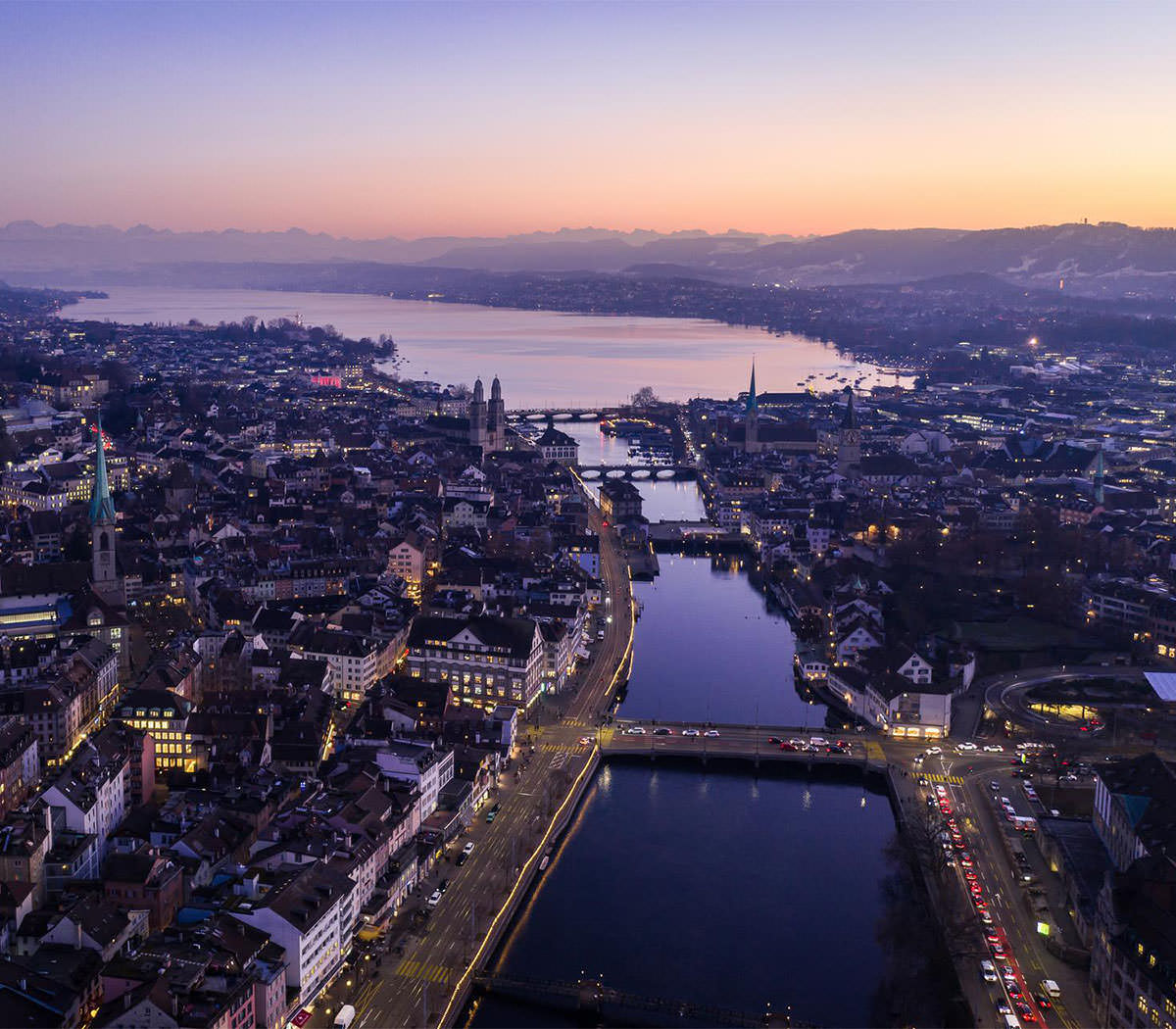
The best fibre network for Switzerland
With an annual investment of around 1.7 billion, Swisscom will enable almost the entire population of Switzerland to access the fibre optic network by 2035. This will also allow the copper network to be switched off and electricity consumption to be significantly reduced. Swisscom will ensure coverage for a small number of customers outside residential areas with state-of-the-art, high-performance mobile and satellite technologies.
The best network
Again and again.
Switzerland’s best fibre network is getting bigger all the time
Discover your possibilities – for using the opportunities of tomorrow
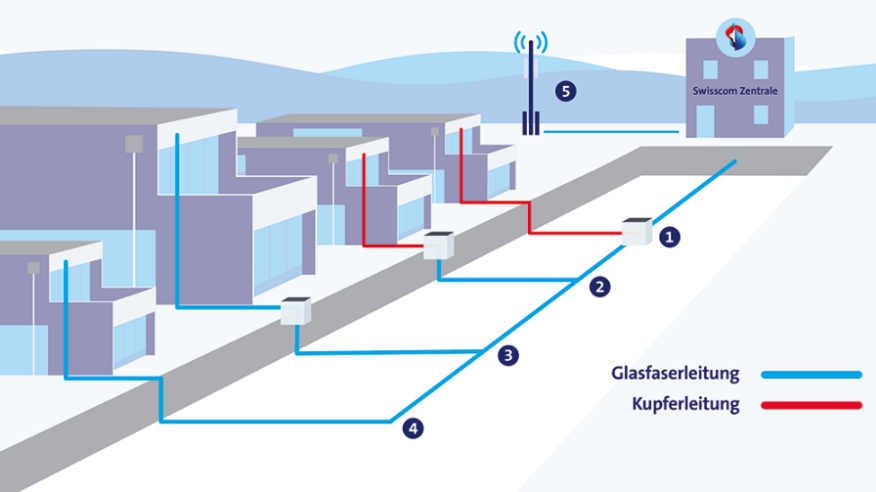
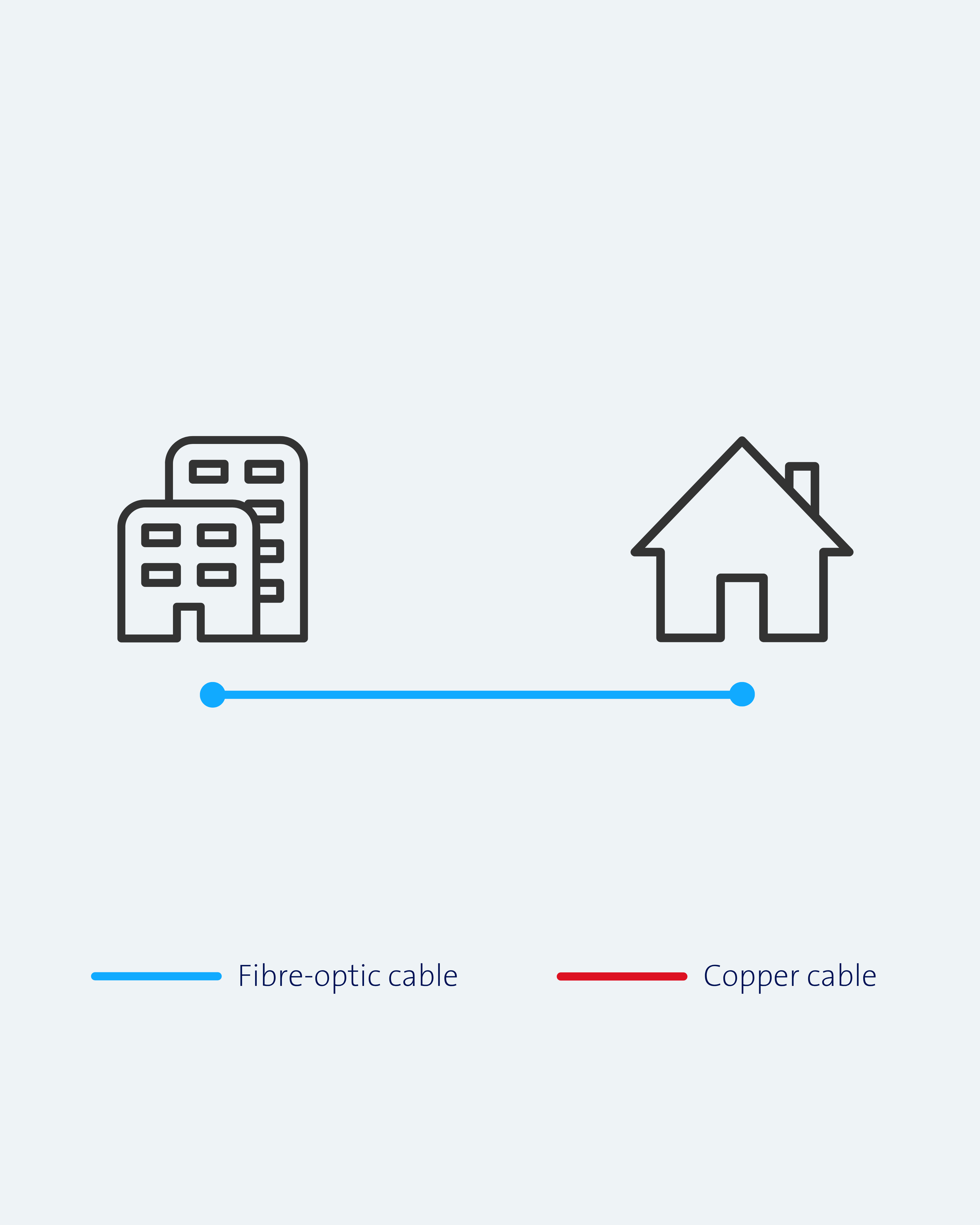
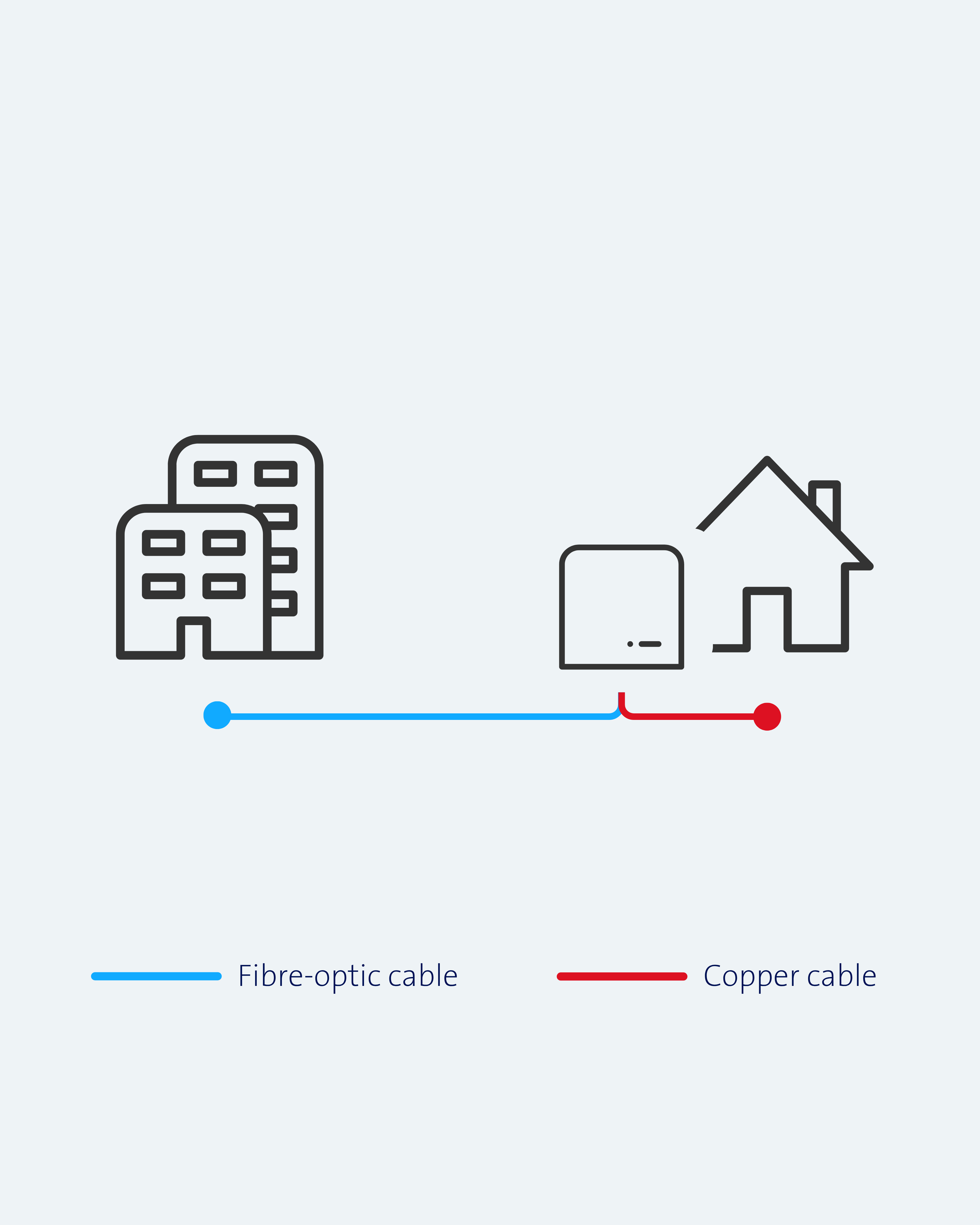
Fibre-to-the-home (FTTH)
Bandwidths in the gigabit range will enable the entire Swiss population in the future to use the highest quality, state-of-the-art digital services at home. To achieve this, Swisscom is modernising its existing fixed and mobile network infrastructure in all Swiss municipalities. By 2035, almost the entire population will have access to the fibre optic network.
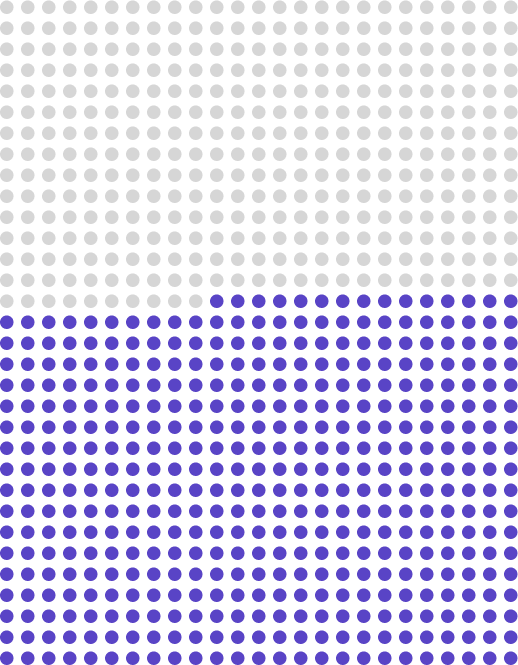
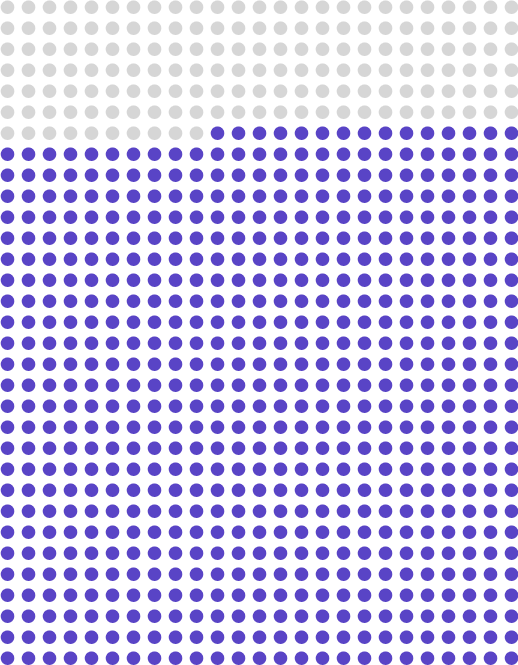
2024: ≈ 50%
2025: ≈ 57%
2030: ≈ 75 – 80%
Status and goal of Swisscom’s fibre optic network expansion to the number of households and businesses in Switzerland.
Glasfaserausbau
Swisscom hat mit den Glasfaserausbau im Jahre xx begonnen, in den vergangenen Jahren hat Swisscom die ganze Schweiz mit verschiedenen Glasfasertechnologien erschlossen, damit viele Kundinnen und Kunden bereits von höheren Geschwindigkeiten profitieren können. Nun baut Swisscom die Schweiz weiter mit FTTH (Fibre to the Home) aus. Kleines FAQ, was es bis anhin für Technologien gab. FTTH, FTTX, FTTB, FTTS, FTTO, FTTC…
Fixed-network technologies at Swisscom
Test your Internet speed
Here you can find out what speed is currently available at your address. Speed data in your municipality and at your address may vary. The reason for this is explained under “Frequently Asked Questions”.
Fibre optic offers at Swisscom
The best network
Climate contribution
Top Smartphones
After around 150 years, the copper era is coming to an end.
Fibre network construction partners
To ensure the swift rollout of our fibre network, we have partnered with four construction firms. And, in many municipalities, we are also collaborating with local businesses such as electricity suppliers and cable network operators.
cablex
cablex is a wholly owned subsidiary of Swisscom. The company employs over 2,500 people and specialises in the construction, maintenance and operation of high-performance ICT and network infrastructure solutions. It also plans and implements forward-looking smart infrastructure projects. As a leading network infrastructure and services company, with over 20 years of experience in the market, cablex has played an important and pioneering role in shaping and developing successful network expansion in Switzerland.
Axians
For 40 years, Axians has been one of Switzerland’s leading providers of planning, implementation and maintenance services for fibre optic and copper cable networks as well as modern wireless, relay and Polycom infrastructures. Axians’ comprehensive ICT solutions portfolio is tailored to meet the challenges of digital transformation. Its approximately 1’000 specialists always keep their fingers on the technological pulse and support numerous customers across the entire ICT process chain at over 20 locations in Switzerland.
Circet
Circet (Schweiz) AG is the Swiss subsidiary of the Circet Group, Europe’s leading provider of design, planning, construction and maintenance services for telecommunications networks. The firm has operated in Switzerland since 2020. Its growth in Switzerland is bolstered by its foreign sister companies, such as those operating in France, Germany and the UK, where FTTH was rolled out to more than 1.8 million households in 2021.
Multinet
Multinet Communication is a leading provider of telecom wireline and wireless services. The company serves various Swiss network operators as a general contractor and offers services covering network design, contract management, engineering, implementation and operations. Multinet Communication can draw on a wealth of experience as it has played an active role in Swisscom's network operations for over 10 years.
Frequently Asked Questions
What technologies are used in the network expansion?
Swisscom is installing Fibre to the Home (FTTH) across Switzerland to increase fibre coverage to around 57% by the end of 2025 and to between 75 and 80% of homes and offices by the end of 2030.
Who is paying for the network expansion?
Swisscom is covering the costs of network expansion.
Network expansion on private property?
If construction work is necessary on private property (e.g. cable routing), Swisscom's construction partner will contact the owner in advance.
Different speed data between municipality and address?
The achievable speeds indicated on the network expansion map for each municipality apply primarily to residential areas. Outside of these areas, the speeds will typically be lower.
Expansion information is sometimes unavailable or changed?
The information about network expansion is automatically adjusted to the expansion status. In exceptional cases, information about an address may not be available. Should this occur, please contact us.
Is it possible to use the Swisscom network to access products from other providers?
Yes, the Swisscom network is open to all providers.
Which providers run on the Swisscom network?
As well as Swisscom, Wingo, Migros Mobile and Coop-Mobile also use the Swisscom network.
Contact for municipalities
Are you a public authority member with questions about network expansion in your municipality? Contact Swisscom, we will be happy to advise you.
Legal information
Unless otherwise specified, the speed data on this website indicates the download rate.
The status “expanded” means that the majority of the households are connected (homes and offices). Additional households may be connected at a later date.
Internet speeds within a municipality may vary due to different fibre-optic technologies or expansion areas.
Swisscom makes every effort to ensure that the availability check is correct. However, Swisscom cannot guarantee that the information provided about network expansion is up-to-date, correct or complete.
Communities as per: 1 January 2023