Sustainability
As a sustainable ICT company, sustainability considerations concerning environmental impact, social aspects and governance have been part of all corporate decision making since our inception.
Our group: Innovating responsibly for positive societal impact.
Group Sustainability strategy 2030
Swisscom Group takes responsibility and addresses country-specific priorities in Switzerland and Italy. We leverage complementary strengths, support each other's development, and drive meaningful progress in sustainability. For today, tomorrow and all our futures. For our journey into a sustainable future, we are guided by the 17 Sustainable Development Goals of the United Nations and living our commitment to sustainable development in all three ESG (environmental, social and governance) areas.
Find out more about sustainability at Fastweb+Vodafone.(opens in new tab)
Our commitment for the planet
We achieve Net-Zero by 2035 and further support our customers' climate ambitions, while contributing to nature.
Our commitment for our community
We take responsibility for society, empowering everyone in the digital world and being an employer of choice where talents thrive.
Our commitment as a responsible leader
We are a trusted corporate citizen who maintains the highest standards in governance, security and ethics.
Background
Discover more background stories about sustainability on blue News.
Go to the Sustainability section of blue News(opens in new tab)
Other topics
Sustainable business
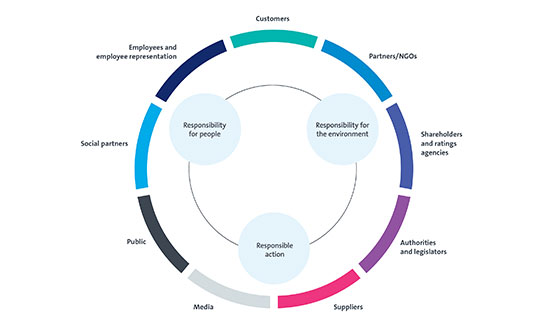
Stakeholders
Key issues
Climate change
Energy
Data Privacy, Security & Ethics
Network Access and Expansion
Circular Economy
Work-life balance
Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
Training and Skills Development
Health and Safety
Workers in value chain
Media Literacy
Protection of children
Business conduct
Pollution
Water and marine resources
Biodiversity and Ecosystems
Affected communities
Top scores in ESG ratings
Contact
Do you have any questions, ideas, constructive criticism? We look forward to your feedback.